Networking!!
Networking!!
Networking or computer networking is a conduit that
connects one node to another (devices) in network information. Networking is
all about connecting, designing, using, managing and operating a network.
The information can be between two users or segments and be sent in a local area
network (LAN) or in a wide area network (WAN) connectivity. Networking works
segments include diverse zones like calls, messages, video streaming, or other
Internet of things (IoT).
Network Types: Networking can be defined in various types on
the basis of designing, layers in the OSI model, components etc. We describe on the
basis of the Physical layer of the OSI Model and Designing.
![]() On the basis of the Physical layer of the OSI
Model:
On the basis of the Physical layer of the OSI
Model:
Wired: The network requires
a physical medium to travel to send the information from one device to another
device. For example usage of ethernet cables in connecting computer devices to
a common network in offices. This type of network is cost-effective, reliable, and durable.
Wireless:
The network doesn’t require a physical medium, as it works on radio
waves to make the information travel from one device to another. For example Wi-Fi. This type of network is mobile, fast, and scalable.
![]() On the basis of the Designing component:
On the basis of the Designing component:
LAN:
Local
Area Network or LAN is a small area network where a group of devices is
connected on a single, geographically limited Network. It can be wired (e.g.
-switch) or wireless (e.g.- Access Points)
WAN:
Wide Area Network or WAN is a wide or larger region network, where multiple
LANs network are connected in the same network. It is not geographically limited
like the LAN.
Network
travels following the OSI 7-layer model or TCP/IP 4 layers model:
Open System Interconnection Model:
The open system interconnection model or OSI model is a
network model which defines how actually information travels from one device
node to another device node. The information travels via 7 layers, from one
stage to another. The 7 layers are as follows:
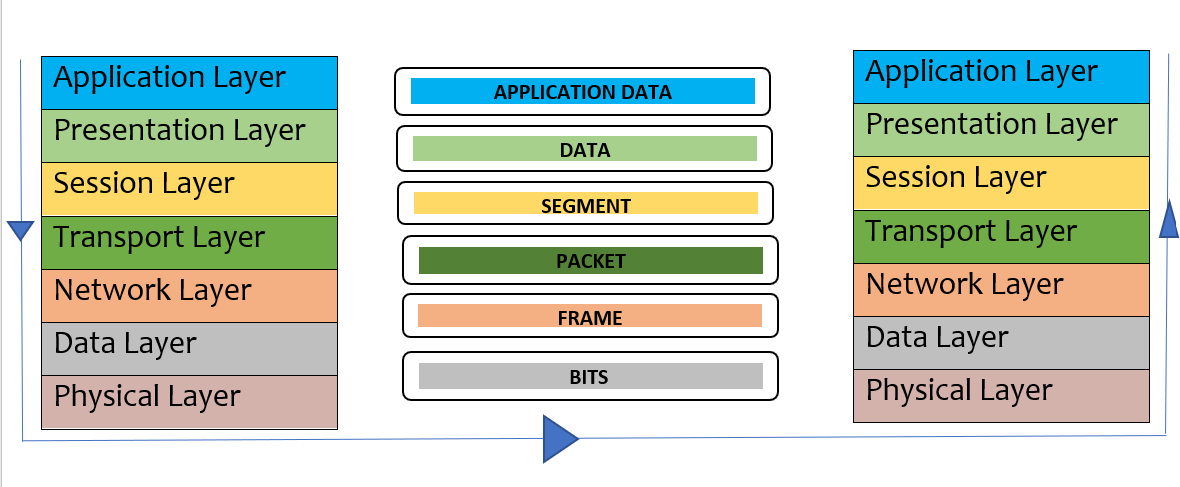
Application
layer>>Presentation layer>>Session layer>>Transport
layer>>Network layer>>Data layer>>Physical layer
Application Layer: The application layer's basic purpose is to provide a user interface for applications. This layer provides network services to the applications running on it. Protocol for this layer is SMTP, HTTP, and FTP.
Presentation Layer: The data from the application layer is extracted here and then sent to the next layer. The function of this layer is to translate, encrypt-decrypt and compress the data. Protocol used in this layer is HTML, XML, and JSON.
Session
Layer: The function of this layer is to establish and
maintenance of the session, authentication, security, and communication between
two devices in half-duplex or full-duplex mode. Protocol used in this layer is RPC and SIP.
Transport
Layer: Data of the transport layer
is called segments. It is the layer responsible for taking services from the network layer and providing services to the application layer. It is actually
responsible for the end-to-end transmission of data in the whole process. At this
layer, the source and destination ports are decided. It makes connectionless
(UDP) or connection-oriented (TCP) pathways depending on which is required. For
example, UDP is used by DNS services while TCP is used for communication which
requires acknowledgment like a query asked by the user. Protocol used in this layer is TCP, UDP, and SCTP
Network
Layer: Transmission of data from
one host to another which might or might be not in the same network zone. The
data here are called packets. It put the source and destination IP address in
the header. The function includes routing and logical addressing. For example Routers and advanced switches. Protocol used in this layer is IP, ICMP, and RIP
Data
Link Layer: The layer's responsibility is
to transfer data from node to node using the Source and destination MAC address.
The receiver’s MAC address is obtained by using a request process called as ARP
(Address Resolution Protocol) onto the wire asking “Who has that IP address”?
and whoever will be the destination host will reply with an acknowledgment. The
data packet here on this layer is called a Frame. The function of the layer
includes framing, physical addressing, error, flow, and access control. Example:
Switch, and Hub all are data link layer devices. Protocol used in this layer is PPP and HDLC.
Physical
Layer: The lowest layer at
receiving end and the upper layer for the sender’s end is the physical layer.
It is a part of the hardware layer and its function is to create an actual physical
connection between devices. The message here comes in form of bits and is
transferred in form of bits only from one node to another node. The function of
the layer includes bits synchronization and rate control, transmission mode,
and physical topologies. For example Hub, modem, cables, repeaters, etc. Protocol used for this layer is Ethernet, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and USB.
![]() Different
protocols followed at each layer:
Different
protocols followed at each layer:
|
LAYER |
NAME |
PROTOCOLS |
|
Layer-7 |
APPLICATION |
SMTP,
HTTP, FTP |
|
Layer-6 |
PRESENTATION |
SSL,
TLS |
|
Layer-5 |
SESSION |
NetBIOS,
SAP |
|
Layer-4 |
TRANSPORT |
TCP,
UDP |
|
Layer-3 |
NETWORK |
ICMP,
ARP |
|
Layer-2 |
DATA |
PPP,
FRAME RELAY, CABLE |
|
Layer-1 |
PHYSICAL |
ISDN,
MACHINES, LAPTOP |
![]() Difference
between OSI and TCP/IP Model:
Difference
between OSI and TCP/IP Model:
|
OSI MODEL |
TCP/IP MODEL |
|
OSI model has a clear distinction among the
interfaces, services, and protocols. |
TCP/IP hasn’t any clear distinguishing
points between services, interfaces, and protocols. |
|
To define routing standards and protocols OSI
model uses the Network layer. |
TCP/IP uses only the Internet layer. |
|
OSI model use two separate layers physical
and data link to define the functionality of the bottom layers |
TCP/IP uses only one layer (link) to
define the functionality. |
|
In the OSI model, only the transport layer is connection-oriented. |
A layer of the TCP/IP model has a major
advantage over OSI and it is both connection-oriented and
connectionless. |
|
In the OSI model, the data link layer and the physical
are separate layers. |
In TCP data link layer and physical layer
are combined as a single host-to-network layer. |
|
The minimum size of the OSI header is 5
bytes. |
The Minimum TCP/IP header size is 20 bytes. |
SUMMARY:
The
OSI Model, TCP/IP model, and networking is a logical and conceptual fundamentals
in the IT field. The model defines network communication as a process used by the systems
in open to interconnection and communication with other systems. As we observed
as well, In the OSI model, a layer should only be created where definite levels
of abstraction are needed, otherwise, no such requirement is observed. OSI layer
helps you to understand communication over a network. Thus, for understanding and work in
networking, one needs to work and understand the fundamentals of Networking



Comments
Post a Comment